FEM03-变分法与最小势能原理
简介
建立连续系统的数学模型,除了采用“FEM02-连续系统的微分方程”中介绍的方法外,还可以采用变分法(variational approach)。变分法的本质是构造泛函求极值。具体是指:构造关于状态变量的泛函(函数的函数)总势能,当泛函的变分为零时,泛函取得极值,即最小势能原理(the principle of minimum potential energy)。
最小势能原理
在线性结构分析中,当把位移作为状态变量时,系统的总势能(total potential energy)Π=U-W。其中,U是系统的应变能(strain energy ),W是载荷的总势能( total potential of the loads)。
注意:W是载荷的总势能,有的教材上认为W是外力的功其实是不正确的,两者并不相等。
考虑刚度为k的弹簧,受到载荷P作用,产生位移u;如果采用直接法建立平衡方程,则有P=ku。
下面讨论变分法的应用,解释最小势能原理。
应变能U=1/2·ku2 (外力的功全部转换为应变能,因此:应变能=外力的功。外力从0逐渐增大到P,弹簧刚度不变的情况下,外力的平均值为P/2,所以外力的功为Pu/2,即1/2·ku2)
载荷的总势能W=Pu (势能的定义:The energy possessed by a body as a result of its position or condition rather than its motion. ——The American Heritage® Science Dictionary )
因此,Π=1/2·ku2-Pu。Π关于u的变分δΠ=(ku-P)δu;δΠ=0时,取极值,总势能最小,则ku-P=0,即P=ku。
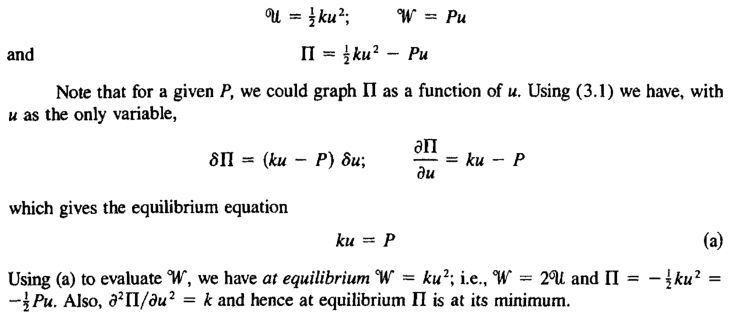
通过以上对单个弹簧的分析,可以看出:变分法推导出来的平衡方程与直接法一致。
下面采用变分法,建立连续系统的数学模型。
考虑“FEM02-连续系统的微分方程”中的例2.3,构造泛函(系统的总势能)如下:
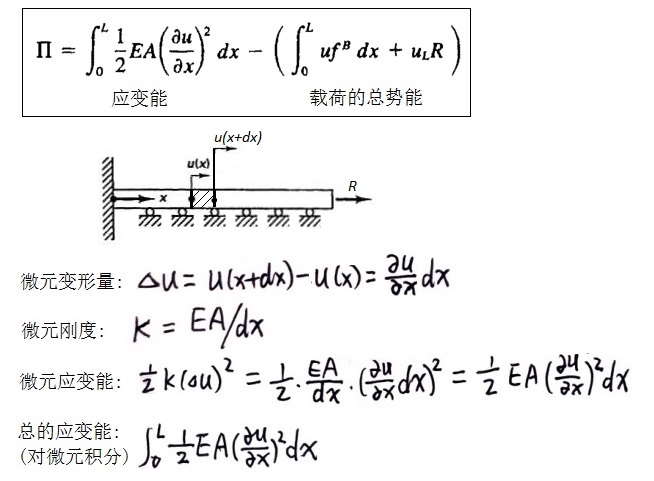
对Π取极值,δΠ=0,得到:

由于δu是任意的,但在给定位移边界条件的u0处δu0=0,所以上式中δu的各项系数均为零。因此,可以得到:
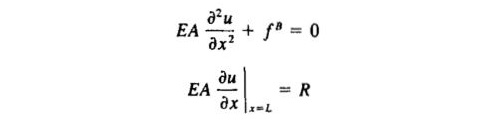
其中,fB=-Aρ ∂2u/∂t2(惯性力)。代入得到控制方程,与直接法的控制方程一致。
本质边界条件和自然边界条件
如果控制方程中状态变量的最高阶导数的阶次是2m,则:“本质边界条件”(essential boundary conditions)中状态变量的最高阶导数的阶次为m-1,“自然边界条件”(natural boundary conditions)中状态变量的最高阶导数的阶次为m至2m-1。我们将该问题称为Cm-1变分问题。

变分法的好处
既然变分法和直接法都得到了一致的结果,我们为什么要采用变分法呢?或者说采用变分法有哪些好处?总结以下几点:
- The variational method may provide a relatively easy way to construct the system-governing equations. This ease of use of a variational principle depends largely on the fact that in the variational formulation scalar quantities (energies, potentials, and so on) are considered rather than vector quantities (forces, displacements, and so on).
变分法可能提供了一种相对而言更加便利的方法来构造系统的控制方程,其便利性体现在:变分公式主要考虑的是标量(能量、势能等)而不是矢量(力、位移等)。 - A variational approach may lead more directly to the system-governing equations and boundary conditions. For example, if a complex system is being considered, it is of advantage that some variables that need to be included in a direct formulation are not considered in a variational formulation (such as internal forces that do no net work).
变分法可以更直接地推导出系统的控制方程和边界条件。例如:对于一个复杂的系统,在直接法中需要考虑的某些量(例如不产生净功的内力),在变分法中并不需要考虑。 - The variational approach provides some additional insight into a problem and gives an independent check on the formulation of the problem.
变分法给出了从另一个角度深入理解问题的方式,并能独立检查建立数学模型的过程。 - For approximate solutions, a larger class of trial functions can be employed in many cases if the analyst operates on the variational formulation rather than on the differential formulation of the problem; for example, the trial functions need not satisfy the natural boundary conditions because these boundary conditions are implicitly contained in the functional.
采用近似解法时,如果处理的是变分形式而不是微分形式,我们可以采用更多类型的试函数。例如:试函数不必满足自然边界条件,因为自然边界条件已经隐含在泛函中。
Reference:
- Finite Element Procedures by Klaus-Jürgen Bathe 轩建平 译
- A First Course in Finite Elements by Jacob Fish & Ted Belytschko